What is difference between Process, Procedure and Processors?
* Process is a flow of execution to
perform a particular task.
* Procedure is a set of instructions representing a particular task.
* Processor is an Hardware Component generating process to
perform task.
* Procedure is a set of instructions representing a particular task.
* Processor is an Hardware Component generating process to
perform task.
What is difference between process and Thread?
Process is heavy weight, it will
take more execution time & more
memory Consumption, it will reduce
applications performance.
Thread is light weight, it will take
less execution time & less
memory Consumption, it will improve application
performance.
What is Multitasking?
Executing several task simultaneously is called multitasking.
Process Based Multitasking -
Executing several tasks simultaneously where each task is separate
independent process such type of multitasking is called process
based multitaksing.
Example: OS Level
Thread Based Multitasking-
Executing several tasks simultanously where each task is a separate
independent part of the same program, is called Thread based
multitasking. And each independent part is called a "Thread".
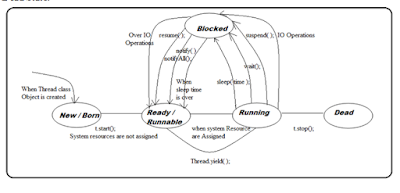
What is Thread, and how many ways we are able to prepare Thread
is in java application?
Thread is a flow of execution, it can be used to perform a particular task.
As per Predefined library provided by java, There are 2 ways to prepare Threads.
Thread is a flow of execution, it can be used to perform a particular task.
As per Predefined library provided by java, There are 2 ways to prepare Threads.
i. Extending Thread Class:
In this approach, we have to declare an user defined class and it
must be extended from java.lang.Thread class
Ex: class MyThread extends Thread
{ ---implementation---- }
ii. Implementing Runnable Interface:
In this approach, we have to declare an user defined class it must
implements java.lang.Runnable interface
Ex: class MyThread implements Runnable
{ ---implementation--- }
Thread Scheduler:
If multiple Threads are waiting to execute then which Thread will execute 1st is decide by "Thread Schedular" Which is part of JVM.
What is difference between
wait() and sleep() method?
wait()
|
sleep()
|
1) The wait()
method is defined in Object class.
|
The sleep() method
is defined in Thread class.
|
2) wait() method
releases the lock.
|
The sleep() method
doesn't releases the lock.
|
What is the difference between notify() and notifyAll()?
The notify() is used
to unblock one waiting thread whereas
notifyAll() method is used to unblock all the threads in waiting state.
Explain Thread class constructors?
There are eight constructors are available in Thread class:
1. Thread t=new Thread();
2. Thread t=new Thread(Runnable r);
3. Thread t=new Thread(String name);
4.Thread t=new Thread(Runnable r, String name);
5.Thread t=new Thread(ThreadGroup g, String name);
6.Thread t=new Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable r);
7.Thread t=new Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable r, String name);
8.Thread t=new Thread(ThreadGroup g, Runnable r, String name, long stacksize);
What is Daemon Thread? And give an example?
The Threads which are running in the background are called
Daemon Thread.
Example: Garbage collector.